July 31, 2024
A Logistic Support Analysis Control Number (LCN) is a code that represents a functional or hardware assembly structure of an end item. Extreme care should be exercised in developing the structure so that the fewest number of characters are used for each indenture level.
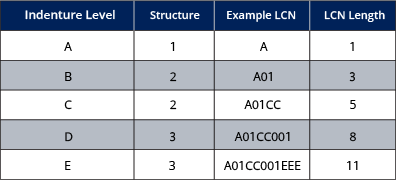
LCN Structure is a number signifying the levels of indenture depth and the width of each level represented by the LCN. The first digit identifies the A indenture level of the LCN. The second digit identifies the B indenture level, and so on.
The number used for each indenture level declares how many digits will make up that level of the LCN structure. A one means only a single digit. A three means three digits wide.
For example, if the LCN Structure is 12233, an LCN must be either 1, 3, 5, 8, 11, or greater than 11 positions.
Functional Breakdown LCNs are used to understand what role a particular item plays within a system. For example, a radio with its wires, transmitter, receiver, volume knobs, attaching hardware, and antenna are part of a communication system. The communication system becomes the basis for the LCN breakdown without any regard to where the parts are physically located. Functional LCNs cannot be Provisioned, but they can be converted to Physical when ready.
Physical Breakdown LCNs are used to understand where an item is located within a system. Use physical breakdown to understand where an item is located, but not what function or role it plays within a system. For example, a radio uses hardware to attach to the cab of a vehicle, the volume knobs and wires attach to the radio, there are wires attaching the radio to the antenna, and the antenna uses hardware to attach to the outside body of the vehicle. Each place where there is physical contact, an LCN would represent the item without regard for the role the item plays in the system. Only Physical LCNs can be Provisioned.
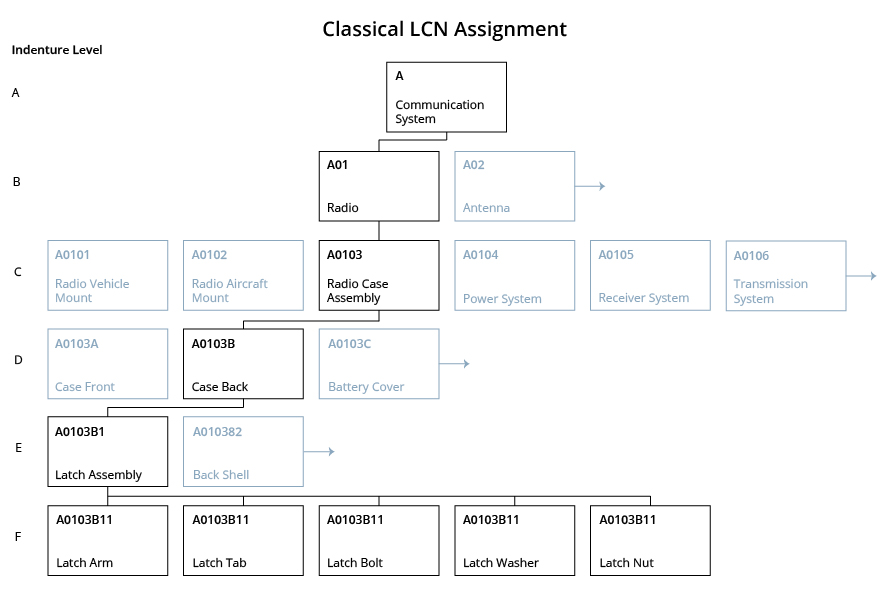
Classical Assignment dictates assignment of a unique LCN to every application of a part numbered item in the system all the way down to the nuts and bolts. This method dictates assignment of a unique LCN to every application of a part numbered item in the system including piece parts. This method ensures proper identification of an item to its Next Higher Assembly (NHA) and ensures proper roll-up of data for all LSAR reports. From a provisioning standpoint, use of the classical assignment method would allow the automatic assignment of Provisioning List Item Sequence Number (PLISN), NHA PLISN, Same As PLISN, and Indenture Code.
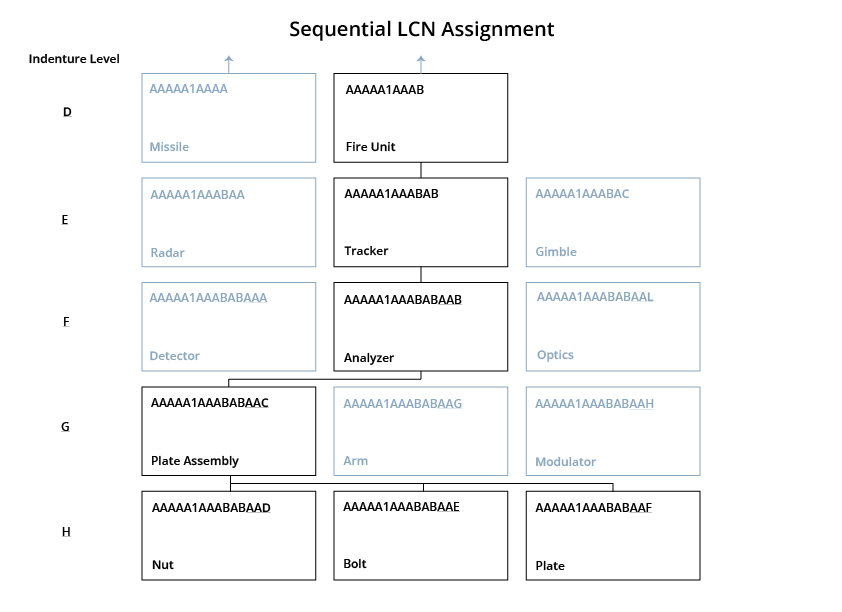
The diagram below traces from Indenture Level A, Communication System, through to Level F, Latch Assembly components for a theoretical system. The LCN Structure is 122111.
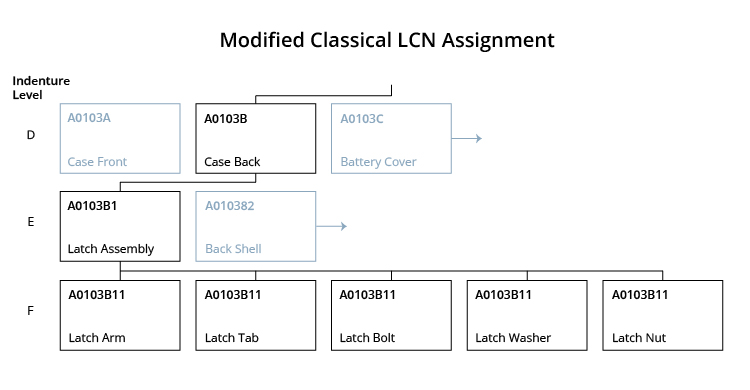
Modified Classical is a variation of the classical assignment method, which permits piece parts with an Item Category Code (ICC) of Y to be assigned the same LCN at the indenture level below the component of which they are part. In addition, attaching hardware (ICC of AE) may be assigned the same LCN at the same indenture level at which the assembly is located. The assembly to which the attaching hardware is required is provided a separate LCN.
Application of this Modified Classical could economize the number of LCNs required at the lower indenture levels. Use of this method ensures proper roll-up of data for all LSAR reports. From a provisioning standpoint, this method allows the automatic assignment of all PLISNs and the indenture code.
The diagram below uses the same radio communication system structure as the Classical Assignment diagram. Notice that Indenture Level F for the Latch Assembly uses the same LCN nomenclature for all its entries.
Sequential Assignment is not an active choice, but rather a default when the above two methods have exceeded 18 characters in the LNC field. For large systems, an attempt to use any of the above methods may still result in a need for more than the 18 characters allocated to the LCN field. In this situation, the classical assignment method could be employed for the first few characters of the LCN field, with the remaining characters assigned sequentially.
This method does not affect the normal processing of the LSAR output reports. However, it is necessary to select reports at indenture levels above the point where sequential assignment of LCNs was initiated. Use this method if more than eighteen indenture levels are needed.